
Twenty nevi on the arms: A simple rule to identify patients younger than 50 years of age at higher risk for melanoma. Tanning lamps and beds emit UV rays and can increase your risk of skin cancer. You might also want to consider clothing that's made with fabric specially treated to block UV radiation. Sunglasses, broad-brimmed hats, long sleeves and other protective clothing can help you avoid damaging UV rays. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using a broad-spectrum, water-resistant sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Apply it generously and reapply every two hours - or more often if you're swimming or sweating. Use a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15. Apply sunscreen about 30 minutes before going outdoors, even on cloudy days. When you are outdoors, seek shade or use a sun-protective umbrella. Try to schedule outdoor activities for other times of the day, even on cloudy days or in winter. For many people in North America, the sun's rays are strongest between 10 a.m. And children who haven't been protected from sun exposure tend to develop more moles. UV radiation has been linked to increased melanoma risk. Take measures to protect your skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, such as from the sun or tanning beds.

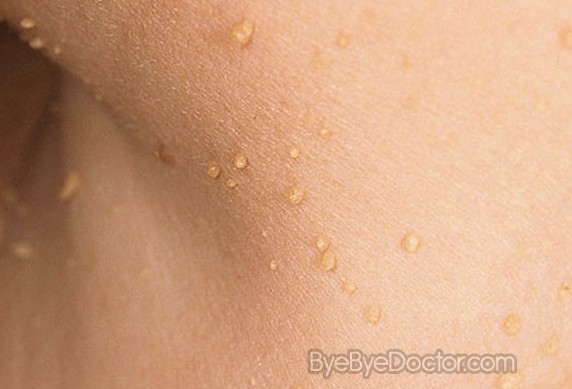
#Multiple skin tags on neck professional#
Talk with your doctor about your risk factors for melanoma and whether you need a professional skin exam on a routine basis.
Also check the genital area and between the buttocks. With the help of mirrors, do a head-to-toe check, including your scalp, palms and fingernails, armpits, chest, legs, and feet, including the soles and the spaces between the toes. Regularly examine your skin to look for changes that may signal melanoma. Watch for changesīecome familiar with the location and pattern of your moles. The following measures can help limit the development of moles and the main complication of moles - melanoma. In addition, some types of atypical nevi lead to a genetic form of melanoma. If you've had melanoma before, you are at increased risk of a mole becoming cancerous. Having a personal or family history of melanoma.Having more than 50 moles indicates an increased risk of melanoma and possibly breast cancer. Moles that are large and irregular in shape are known as atypical (dysplastic) nevi. Even a large mole seldom becomes cancerous. On an infant, such moles are classified as large if they're more than 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter. These types of moles are called congenital nevi. Factors that increase melanoma risk include: Some people have higher-than-average risk of their moles becoming cancerous and developing into melanoma. Melanoma is the main complication of moles. They produce melanin, the natural pigment that gives skin its color. Melanocytes are generally distributed throughout the skin. Moles are caused when cells in the skin called melanocytes grow in clusters. It's produced in cells called melanocytes. Melanin is a natural pigment that gives your skin its color. Make an appointment with your doctor if a mole looks unusual, grows or otherwise changes. Others may have only one or two unusual characteristics. Some may show all of the changes listed above. Moles may also evolve to develop new signs and symptoms, such as itchiness or bleeding.Ĭancerous (malignant) moles vary greatly in appearance. Watch for moles that change in size, shape, color or height. Look for new growth in a mole larger than 1/4 inch (about 6 millimeters). Look for growths that have changed color, have many colors or have uneven color. Look for moles with irregular, notched or scalloped borders. This ABCDE guide can help you remember what to watch for: Unusual moles that may indicate melanomaĪ mole may be a sign of skin cancer if it has irregular borders or an asymmetrical shape or if it changes in color, shape, size or height. Flesh moles don't carry a risk of melanoma, but they can be treated if you consider them a cosmetic concern. Dermatoses papulosa nigra are more common among Black women. With hormonal changes in adolescence and pregnancy, they may become darker and larger.Ĭlusters of brown spots around the eyes, cheeks and nose are sometimes called flesh moles, but they are actually dermatoses papulosa nigra - a type of seborrheic keratosis, not clusters of pigment-forming cells (nevi). Moles can develop anywhere on your body, including your scalp, armpits, under your nails, and between your fingers and toes. Those present at birth (congenital nevi) can be bigger than usual, covering part of the face, torso or a limb. Moles are usually less than 1/4 inch (about 6 millimeters) in diameter - the size of a pencil eraser. They can be smooth, wrinkled, flat or raised. Moles can be brown, tan, black, blue, red or pink. But moles come in different colors, shapes and sizes:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
